Shock Wave Therapy Wimbledon - Focused & Radial ESWT At Wimbledon Clinic Physio
What is ESWT / Shock Wave?
Shock Wave Therapy is a beacon of hope for many dealing with injuries and long-term pain.
It's non-invasive, doesn't rely on painkillers, and can lead to quick relief and recovery.
Originally known as Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT), shock wave therapy is now commonly known as shock wave therapy.
The treatment employs a generator to emit high-energy acoustic (sound) waves. The waves are rapid and pulsed like musical notes into the affected area. While this expresses magic, the power of the soundwaves vibrates the tissues to a high degree at specifically targeted locations, causing profound changes.
These sound waves numb nerve endings to alleviate pain and enhance blood flow to the area. But more than that, the sound waves break down thicker scar tissue or calcifications that stop tendons and muscles from healing. This is why its most well-known use is in the treatment of kidney stones or calcifications that block us from peeing. The new units are modified for orthopaedic and sports injury treatment, creating a light in a previously dark tunnel of conditions.
Shock wave therapy produces carry-over effects; over time, this therapy aids cell regeneration, tissue repair, and pain reduction.
Wimbledon Clinic Physio ensures a professional and effective treatment delivery, making it an ideal alternative to surgeries or steroids.
Whether you're considering Radial or Focused Shock Wave Therapy, understanding their intricacies can help you make a better-informed decision tailored to your needs. Read on to explore the different types of shock wave therapy (ESWT)
Comparing Radial vs Focused Shock Wave Therapy at Wimbledon Clinic
Dive into the world of shock wave therapy in Wimbledon, London, as offered by Wimbledon Chiro & Sports Injury Clinic. Discover the non-invasive alternative to many surgical or steroid-related procedures and understand the nuances of each technique.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) comes in two primary 'flavours':
- Radial ESWT
- Focused ESWT
Focused Shock Wave Therapy

Radial Shock Wave Therapy
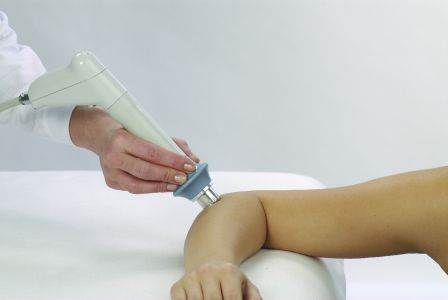
But what are the differences? How do they tackle different pain points and limb function problems? Read on, or if you’re unfamiliar with ESWT, use the glossary below to get the basics.
Glossary Of Terms
Shock wave therapy, or extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT), is a non-invasive medical treatment used to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, particularly those involving connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments. Its wave is delivered into the treatment area with two types of machine generators. These generators give two kinds of ESWT: 1) Focused and 2) Radial. Here's a brief overview:
1. **Mechanism**: Shock wave therapy uses high-energy sound or acoustic waves to induce microtrauma in the tissue. This microtrauma initiates a biological response in the treated area, which includes increased blood flow and the stimulation of cell regeneration and healing processes.
2. **Conditions Treated**: Shock wave therapy is typically used for conditions like plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, shoulder tendinitis, Achilles tendinitis, and other chronic tendinopathies. It's also used in some cases for bone healing and other orthopaedic conditions.
3. **Procedure**: it should be noted that there are two types of shock wave therapy wave generators, although the procedure is the same as the client's experience. During the treatment, a device generates shock waves directed to the affected area through the skin. A trained therapist can adjust the intensity and frequency of the waves. Usually, the procedure is done in a series of sessions and does not require anaesthesia.
4. **Benefits**: The main benefits include pain reduction and improved mobility in the affected area. It is a non-invasive option compared to surgery and usually has minimal side effects.
5. **Side Effects**: Some patients may experience temporary soreness or swelling in the treated area, but severe side effects are rare.
6. **Effectiveness**: Research has shown varying levels of effectiveness, often dependent on the specific condition being treated. Shock wave therapy, whether the focused or radial type, is generally considered a viable option when traditional treatments like physical therapy or medications have not been successful.
It's important to note that a trained healthcare professional should administer shock wave therapy, and it may not be suitable for all individuals, such as those with certain medical conditions or pregnant women.
Shock wave therapy uses high-energy sound or acoustic waves to induce microtrauma in the tissue. This microtrauma stimulation is similar to what happens when we exercise and impose demands on body tissues that we want to improve.
This microtrauma initiates a biological response in the treated area, which includes increased blood flow and the stimulation of cell regeneration and healing processes.
This is typically required due to healing stagnation which is common in tendon tissues or tissues with anatomically less blood supply.
Think of the pale bits in an anatomy diagram.
When pain causes are ongoing, like the sports you play or the fact you stand for a living. It means healing gets delayed.
If healing doesn't happen within eight weeks, the blood supply reduces, and healing stagnation happens, which slows the healing response and blood supply; ESWT restarts your natural healing process in certain areas of the body when it stagnates.
Radial Shock Wave Therapy (RSWT)
Radial waves predominantly consist of three components:
- Ultrasonic pulses
- Audio acoustic pulses
- Slow shear waves
Its defining feature is that the energy is strongest at the source and diminishes as it moves farther from the source or delves deeper into the skin.
The Radial Applicator: This gun-like tool houses a barrel where a projectile is accelerated. When this projectile hits the applicator tip, an energy pulse forms. This energy transmits as a ‘radial wave’ over the treated area. Its strength is highest at the point of impact but gradually reduces as it penetrates deeper.
Key Takeaway: Radial ESWT is optimal for skin or superficial conditions.
Focused Shock Wave Therapy (FSWT)
Going deeper than its radial counterpart, FSWT zeroes in on areas covered in muscle (hip areas, shoulder areas, etc.) and at shallow depth (elbow, plantar fascia). The focused type uses a cone of crystals, which, when electrified, focuses the energy into a concentrated zone. This focused energy retains its strength as it moves deeper into the body.
Its precision allows it to target issues deep within the body, especially the hips and lower limbs.
Key Benefits:
- Improved effectiveness
- A more comfortable experience due to minimal skin impact
- Higher doses can often be used due to comfort levels and receive twice the treatment stimulation.
Comparing Radial vs Focused Shock Wave Therapy on Depth
With depth being a prime factor, focused ESWT reigns supreme for deep-seated issues like hamstrings or hips.
The Physics Behind Each:
- Radial waves spread over a wide area and usually have a depth of around 3-4cm.
- Focused waves have an adjustable depth ranging from 2 to 30cm.
Pain Levels in RSWT vs FSWT
Typically, RSWT can be more painful due to its application method, making FSWT a preferred choice for many, especially in acute cases.

Session Numbers
Experience has shown that Radial ESWT might need more sessions than Focused ESWT. At Wimbledon Clinic, F-ESWT typically needs fewer sessions than R-ESWT.
How Does Shock Wave Therapy Work?
Shock Wave Therapy (SWT) at Wimbledon Clinic Physio represents a cutting-edge approach to pain relief and tissue healing. This section delves into the sophisticated technology behind SWT and its profound physiological effects, guiding you towards understanding which type of SWT best suits your needs.
The Technology Behind SWT
SWT is categorized into two main types: Radial Shock Wave Therapy (RSWT) and Focused Shock Wave Therapy (FSWT). Each employs unique technology to target pain:
- Radial Shock Wave Therapy (RSWT) uses a pneumatic system to generate shock waves that spread out radially. This technology is ideal for treating superficial layers of tissue, making it practical for conditions close to the skin's surface.
- Focused Shock Wave Therapy (FSWT) utilizes electromagnetic technology to produce high-precision shock waves that can be directed deep into the tissues. This method is beneficial for reaching deeper structures such as tendons, muscles, and joints, providing targeted relief and healing.
Physiological Effects and Healing
When shock waves are applied to an affected area, they stimulate a cascade of biological effects, which include:
- Pain Reduction: SWT works by overstimulating nerve endings, temporarily reducing their ability to transmit pain signals.
- Increased Blood Flow: The shock waves induce microtrauma in the tissue, which promotes increased blood flow and the formation of new blood vessels. This enhanced circulation brings essential nutrients and oxygen for natural tissue healing.
- Cellular Level Changes: SWT prompts the release of growth factors and the activation of stem cells in the treated area. These factors are instrumental in repairing damaged tissue and regenerating healthy cells.
- Breakdown of Scar Tissue: In chronic conditions, SWT helps break down the build-up of fibrous scar tissue, which can restore mobility and alleviate discomfort.
Integrating SWT into Your Treatment Plan
Understanding the nuances between Radial and Focused SWT can help you and your physiotherapist decide the best approach for your condition. Whether alleviating superficial discomfort or targeting deep-seated pain, SWT at Wimbledon Clinic Physio offers a non-invasive solution that accelerates recovery and enhances the body's natural healing processes.
Incorporate this innovative treatment into your recovery regimen and experience a swift return to optimal health. Schedule a consultation today to explore how Focused or Radial Shock Wave Therapy can be tailored to your needs.
Focused Shock Wave Therapy
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy using a BTL Focused Unit
-
Consultation:
£65 (Diagnosis & Plan Of Management, Digital Rehab Is Also Provided)
-
3 x Foucsed Shockwave Therapy session pack:
£348.00 (equ, £116 per session)
-
Additional Focused Shock Wave Sessions::
Maybe required as addition to tradnitional Physio or after 3 session (average))£99
-
Radial Shock Wave Sessions::
This is older technology, which is less effcient and more uncomfoatble - hence is changed at lower price point£99
Book Today!
Do you wish to explore Shock Wave Therapy for your condition at Wimbledon Clinic? Click on the contact button below.